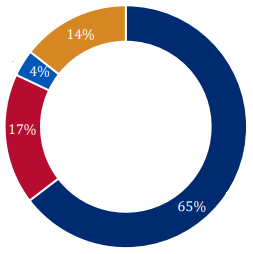
In today’s interconnected world, where technology permeates every aspect of business operations, ensuring robust cybersecurity has become a critical priority for large organizations and their contingent workforce programs.
Cybersecurity encompasses a range of practices, processes and technologies designed to protect digital systems, networks and data from unauthorized access, damage or theft. As cyber threats continue to evolve and grow in sophistication, it is imperative for CW programs to implement comprehensive cybersecurity processes and procedures. Here are the top five reasons you should prioritize cybersecurity, followed by some practical steps you can take within your CW program.
Safeguard sensitive data. Large organizations typically handle vast amounts of sensitive data, including customer information, trade secrets and financial records. Implementing robust cybersecurity measures helps protect this valuable data from falling into the wrong hands, ensuring your customers’ trust while complying with regulatory requirements and safeguarding your intellectual property.
Prevent financial losses. Cyberattacks can lead to significant financial losses for organizations. Breaches can result in direct financial theft, legal liabilities, business disruption and damage to reputation — all of which can have long-lasting consequences. By implementing effective cybersecurity processes, you can mitigate the risks associated with cyberthreats and prevent potential financial damage.
Maintain business continuity. A cyberattack could cripple a CW program and the wider organization, leading to costly downtime and disrupted services. Having robust cybersecurity processes and procedures in place ensures business continuity by minimizing the impact of cyber incidents, facilitating swift recovery and reducing the potential for prolonged disruption.
Protect intellectual property. Intellectual property — including patents, trademarks and proprietary technologies — forms the foundation of many large organizations. Cybersecurity measures help safeguard these valuable assets by preventing unauthorized access, theft or sabotage, ensuring a competitive edge and preserving market position.
Safeguard reputation and trust. In today’s digitally driven marketplace, maintaining a strong reputation and building trust with customers, partners and stakeholders is paramount. A cyberbreach can have severe reputational implications, eroding customer confidence and damaging brand image. By prioritizing cybersecurity, organizations demonstrate their commitment to protecting sensitive information, enhancing customer trust and upholding their reputation.
Here are 10 actions you can take to help protect your business and your CW program.
- Contractual agreements. Include cybersecurity clauses in contracts with external workers, specifying their responsibilities for protecting sensitive information and consequences for any breaches. Ensure compliance with relevant data protection regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation.
- Access control. Ensure that external workers have appropriate access rights to only the systems and data they need for their tasks. Implement strong authentication mechanisms and enforce the principle of “least privilege” to limit their access.
- Data protection. Clearly define and communicate data handling and protection policies to external workers. Require them to sign nondisclosure agreements and provide training on data privacy and security best practices.
- Secure remote access. If external workers require remote access to communities of practice networks or systems, ensure they use secure methods such as virtual private networks, two-factor authentication and encrypted connections.
- Secure communication. Encourage or enforce the use of encrypted channels such as secure messaging apps or email encryption for communication involving sensitive information. Discourage the use of insecure public Wi-Fi networks for work-related tasks.
- Malware protection. Verify that external workers have up-to-date antivirus software installed on their devices and require regular scanning for malware. Also, consider implementing controls to prevent the use of unauthorized or potentially compromised devices on your network.
- Data transfer and storage. Establish guidelines for secure data transfer and storage when external workers handle sensitive information. Encourage the use of secure file transfer protocols or cloud storage solutions with strong encryption and access controls.
- Monitoring and auditing. Implement monitoring mechanisms to track the activities of external workers accessing your systems or data. Regularly review access logs and perform audits to detect any suspicious or unauthorized activities.
- Incident response. Have an incident response plan in place that includes provisions for handling security incidents involving external workers. Clearly define the reporting process and establish protocols for investigating and mitigating potential breaches.
- Regular evaluation. Continuously assess the cybersecurity practices and controls of external workers. Regularly review and update your organization’s policies and procedures to adapt to evolving threats and best practices.
The level of security required will vary depending on the sensitivity of the data and systems being accessed by external workers. It’s important to establish clear guidelines, communicate expectations and ensure ongoing vigilance to protect your organization’s assets.