US Equal Employment Opportunity laws do not prevent an employer from requiring all employees physically entering the workplace to be vaccinated for Covid-19, though the reasonable accommodation provisions of Title VII of the Civil Rights Act, the Americans with Disabilities Act and other EEO considerations do apply. This is among Covid-19 guidance provided by the EEOC on May 28.
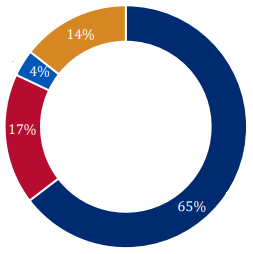
Still, most employers are refraining from making such mandates, according to a survey by Fisher Phillips. Eighty-three percent of employers surveyed indicated that they are neither mandating nor considering mandating that some portion of their workforce receive a Covid-19 vaccine. However, 75% are strongly encouraging it.
Because temporary staff typically would share spaces with the organizations’ directly employed workers, any CW program policies would need to be established in partnership with HR as well as their staffing providers. And while a program’s staffing providers would be responsible for much of the compliance with regard to supplied workers, programs with direct-sourcing components may need to ensure compliance with regard to those workers. Legal counsel should also be consulted.
The EEOC’s guidance breaks down employer obligations in relation to the ADA, Title VII and the Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act. The following questions are answered or updated online:
- May an employer require all employees physically entering the workplace to be vaccinated for Covid-19?
- What are some examples of reasonable accommodations or modifications that employers may have to provide to employees who do not get vaccinated due to disability; religious beliefs, practices, or observance; or pregnancy?
- How can employers encourage employees and their family members to be vaccinated without violating the EEO laws, especially the ADA and GINA?
- Is information about an employee’s Covid-19 vaccination confidential medical information under the ADA?
- May an employer require a Covid-19 vaccination for all employees entering the workplace, even though it knows that some employees may not get a vaccine because of a disability?
- If an employer requires Covid-19 vaccinations for employees physically entering the workplace, how should an employee who does not get a Covid-19 vaccination because of a disability inform the employer, and what should the employer do?
- If an employer requires employees to get a Covid-19 vaccination from the employer or its agent, do the ADA’s restrictions on an employer making disability-related inquiries or medical examinations of its employees apply to any part of the vaccination process?
- Are there circumstances in which an employer or its agent may ask disability-related screening questions before administering a Covid-19 vaccine without needing to satisfy the “job-related and consistent with business necessity” standard?
- Is it a “disability-related inquiry” for an employer to inquire about or request documentation or other confirmation that an employee obtained the Covid-19 vaccine from a third party in the community, such as a pharmacy, personal healthcare provider, or public clinic?
- May an employer offer voluntary vaccinations only to certain groups of employees?
- What should an employer do if an employee who is fully vaccinated for Covid-19 requests accommodation for an underlying disability because of a continuing concern that he or she faces a heightened risk of severe illness from a Covid-19 infection, despite being vaccinated?
- How should an employer respond to an employee who communicates that he or she is unable to be vaccinated for Covid-19 (or provide documentation or other confirmation of vaccination) because of a sincerely held religious belief, practice, or observance?
- What should an employer do if an employee chooses not to receive a Covid-19 vaccination due to pregnancy?
- Is Title II of GINA implicated if an employer requires an employee to receive a Covid-19 vaccine administered by the employer or its agent?
- Is Title II of GINA implicated when an employer requires employees to provide documentation or other confirmation that they received a vaccination from a doctor, pharmacy, health agency, or another healthcare provider in the community?
- May an employer offer an incentive to employees to voluntarily provide documentation or other confirmation that they received a vaccination on their own from a pharmacy, public health department, or other healthcare provider in the community?
- May an employer offer an incentive to employees for voluntarily receiving a vaccination administered by the employer or its agent?
- May an employer offer an incentive to employees to provide documentation or other confirmation that they or their family members received a vaccination from their own healthcare provider, such as a doctor, pharmacy, health agency, or another healthcare provider in the community?
- May an employer offer an incentive to employees in exchange for the employee getting vaccinated by the employer or its agent?
- May an employer offer an incentive to an employee in return for an employee’s family member getting vaccinated by the employer or its agent?
- May an employer offer an employee’s family member an opportunity to be vaccinated without offering the employee an incentive?